Table of Contents
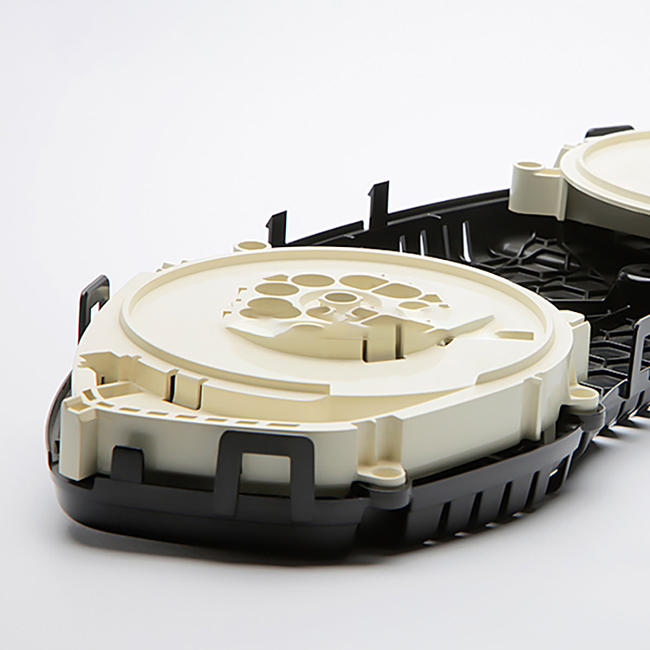
Post-Processing Techniques
- Trimming: Excess material, such as sprues and runners, is removed after the part is ejected from the mold.
- Painting and Coating: ABS parts can be painted or coated to improve appearance and add additional protection. Pre-treatment may be required to ensure good adhesion.
- Assembly: In cases where parts are part of an assembly, additional steps like ultrasonic welding, adhesive bonding, or mechanical fastening may be used.
- Surface Treatments: Techniques like chrome plating or texturing can be applied to enhance the appearance or functionality of the ABS parts.

Environmental Considerations
- Recycling: ABS is recyclable and can be processed into new materials. The recycling process involves grinding used ABS parts into pellets and then reprocessing them into new parts.
- Biodegradability: ABS is not biodegradable. However, efforts are being made to develop more sustainable alternatives and improve recycling processes.
Applications and Innovations
- Medical Devices: ABS is used in medical applications where strength and cleanliness are critical. Innovations in the field include creating intricate parts for diagnostic devices and equipment housings.
- Consumer Products: Innovations include customizable and ergonomic designs for personal gadgets and home appliances.
- 3D Printing: ABS is a popular material for 3D printing due to its ease of use and strong mechanical properties, enabling rapid prototyping and low-volume production.