Table of Contents
Prototype Tooling Overview
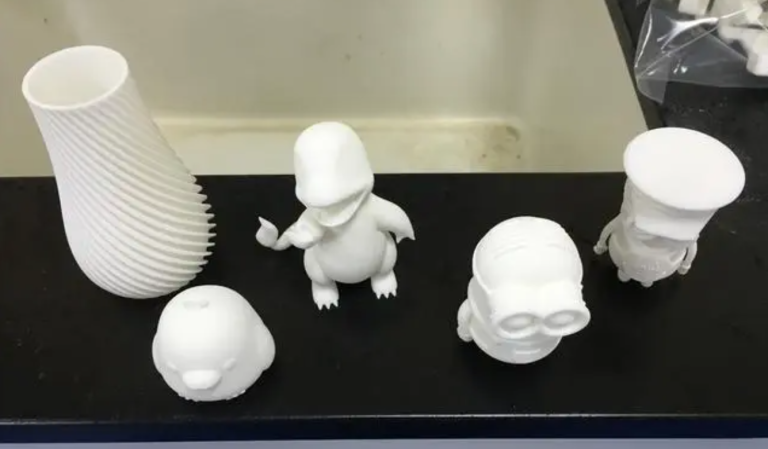
- Purpose: Prototype tooling is used to create molds, dies, or patterns that are essential for manufacturing prototype parts. These prototypes help in testing and validating designs before mass production.
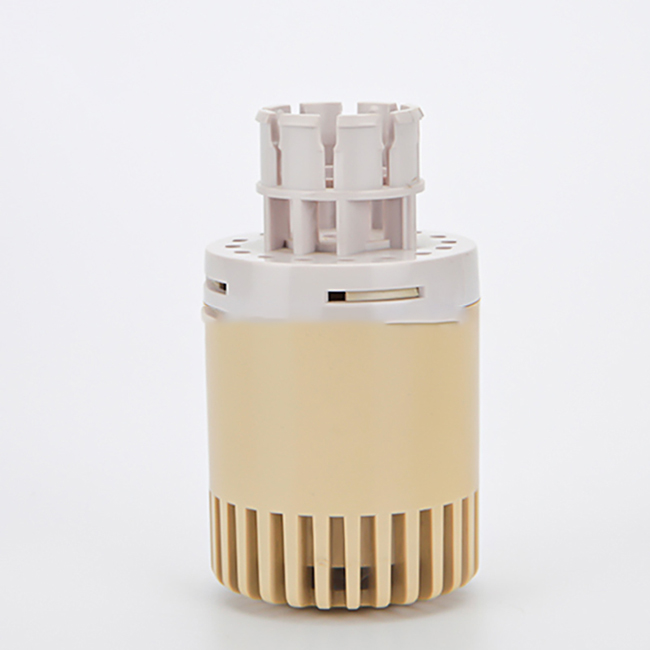
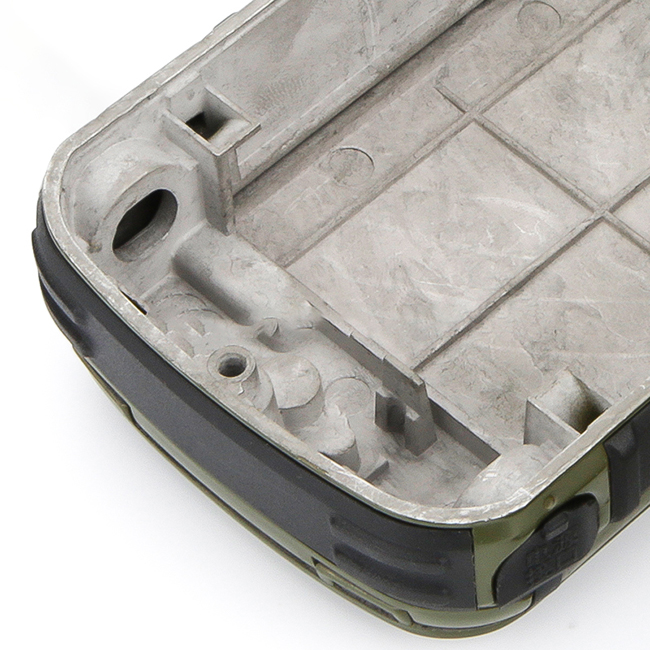
- Materials: For plastic automotive prototypes, the tooling materials are typically chosen based on the specific requirements of the part being developed. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and various types of resins or plastics for mold making.
- Process: The process begins with CAD (Computer-Aided Design) models of the part. These models are used to design the tooling, which can range from simple molds to complex multi-cavity injection molds for producing multiple parts simultaneously.
Importance in Automotive Prototyping
- Speed: Prototype tooling allows for rapid iteration and testing of designs. It helps automotive engineers and designers to quickly assess the functionality and fit of parts, making necessary adjustments early in the development cycle.
- Cost Efficiency: While initial tooling costs can be significant, they are usually lower than those for production tooling used in mass manufacturing. This cost-effectiveness is crucial for companies looking to minimize expenses during the design validation phase.
- Quality Assurance: By producing prototypes with tooling that closely simulates production conditions, automotive manufacturers can better predict how parts will perform in real-world applications. This helps in identifying and resolving potential issues early on.
- Customization: Prototype tooling allows for customization and adaptation of designs based on test results and feedback, ensuring that final production parts meet performance, safety, and regulatory standards.






