Table of Contents
1. Design Creation
- CAD Modeling: The process typically starts with creating a 3D digital model using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This model defines the shape, dimensions, and details of the prototype.
2. Preparation for Printing
- Slicing: The CAD model is sliced into thin horizontal layers using slicing software. Each layer is a cross-section of the final prototype.
3. Printing Process
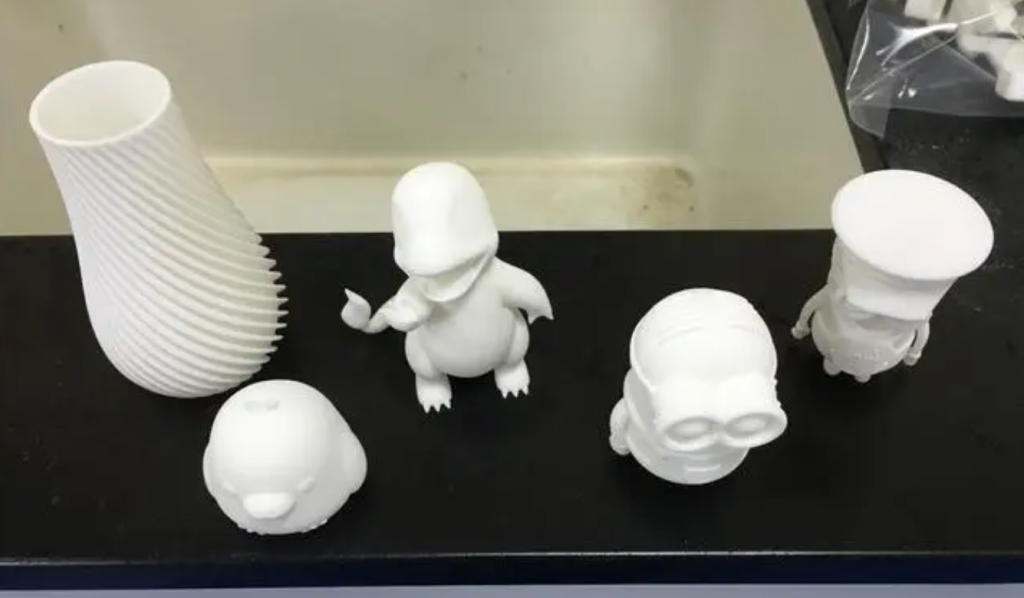
- 3D Printing: The sliced layers are sent to a 3D printer, which then builds the prototype layer by layer. There are various technologies used in 3D printing, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and others.
4. Post-Processing
- Support Removal: Depending on the printing technology, supports or scaffolding may need to be removed manually or using additional tools.
- Surface Finishing: Prototypes may undergo post-processing steps like sanding, painting, or additional treatment to achieve the desired finish.
Benefits of 3D Rapid Prototyping:
- Speed: Designs can be created and produced rapidly, reducing the time required for product development.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to traditional prototyping methods, 3D printing can be more cost-effective, especially for low-volume production.
- Iterative Design: It allows for quick iterations and modifications based on testing and feedback, enhancing the design process efficiency.
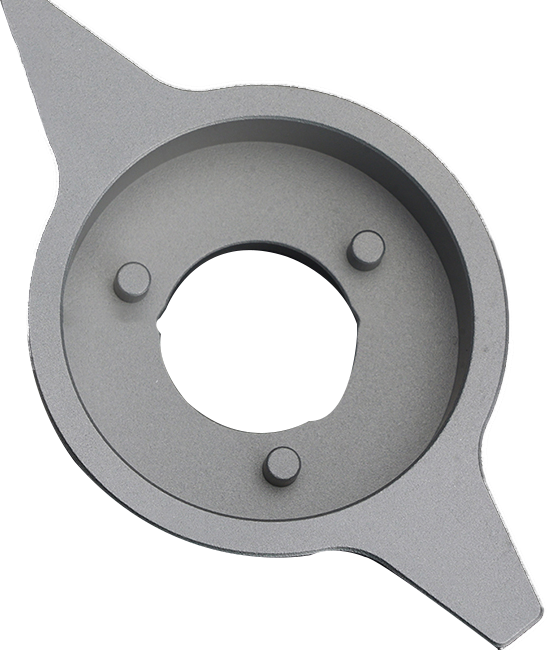
- Complex Geometries: 3D printing enables the creation of intricate and complex geometries that may be challenging or impossible with traditional manufacturing methods.
Applications:
- Product Development: Testing and validating product designs before mass production.
- Engineering: Creating functional prototypes for testing mechanical properties and performance.
- Customization: Designing personalized products tailored to specific customer needs.