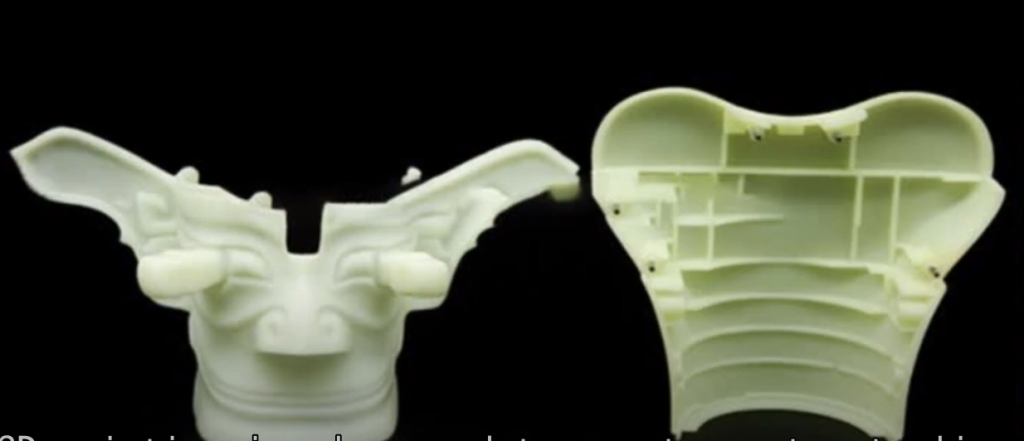
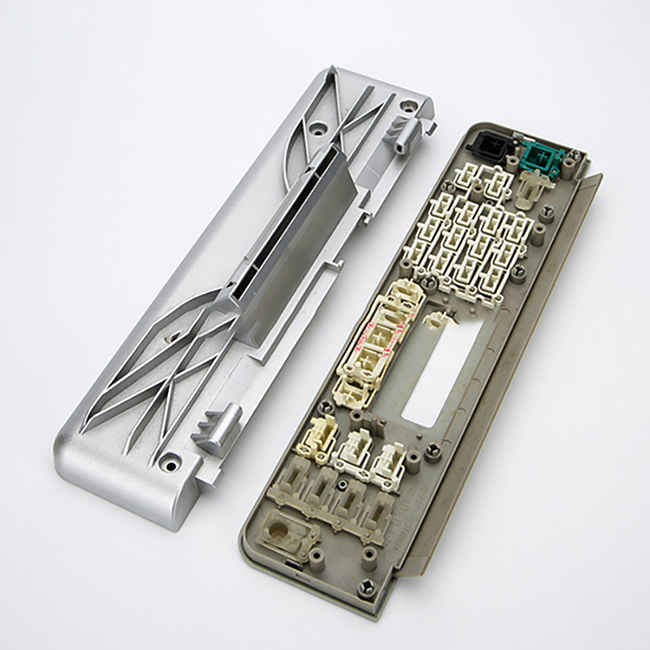
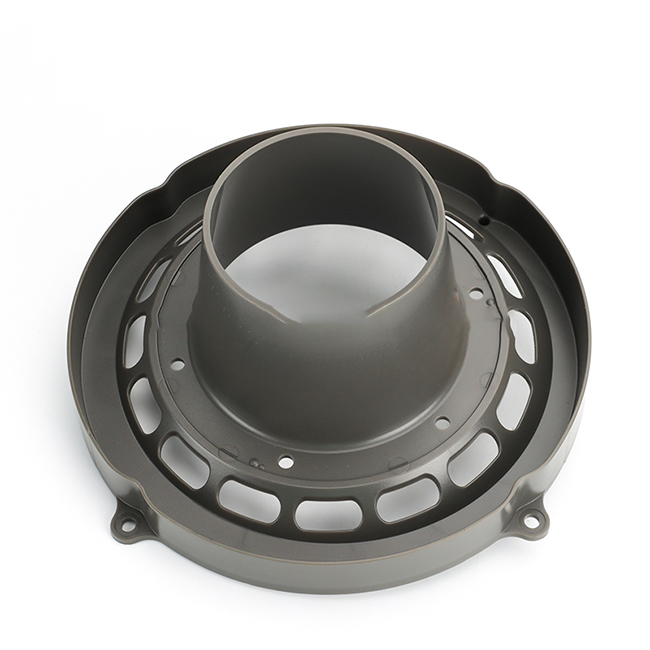
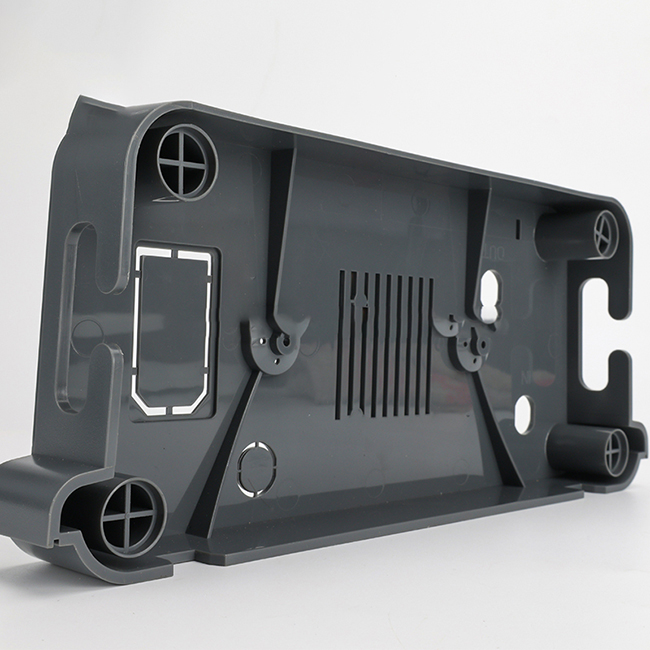
- Rapid Iteration: It allows for quick iterations of designs based on feedback and testing, speeding up the product development cycle.
- Cost-Effective: Producing a small batch of prototypes reduces initial tooling costs compared to traditional manufacturing methods, which can be expensive for low volumes.
- Customization: Prototypes can be customized easily to test different variations of a design or to meet specific requirements.
- Material Variety: There are various plastic materials available for rapid prototyping, each suited to different functional and aesthetic requirements.
- Testing and Validation: Prototypes can be used for functional testing, fit testing, and user testing to ensure the final product meets performance expectations.
- Market Testing: Low volume manufacturing allows companies to introduce new products to the market quickly and gather early feedback from customers.
- Scale-up Readiness: Once a design is finalized, the transition to full-scale production is smoother and more efficient, as potential issues have been identified and addressed during prototyping.
- Reduced Lead Times: Rapid prototyping technologies such as 3D printing can significantly reduce lead times compared to traditional manufacturing methods, enabling faster product launches.
- Design Verification: Prototyping helps verify the manufacturability of a design, identifying potential challenges or improvements before investing in mass production.
- Bridge to Production: It serves as a bridge between initial concept development and full-scale production, allowing companies to refine designs and processes incrementally.