Inhoudsopgave
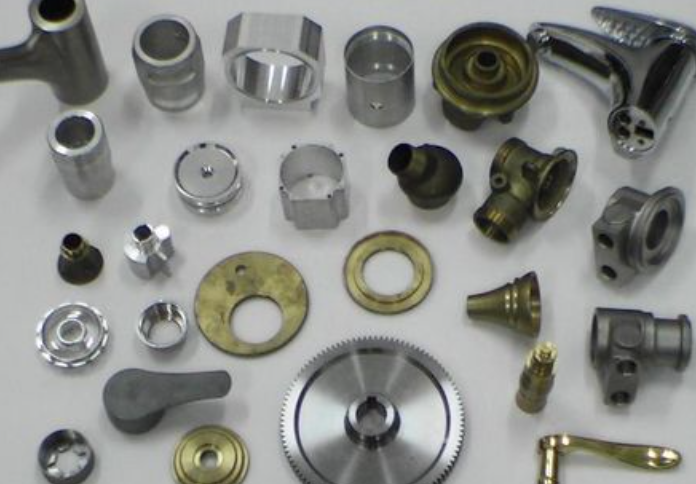
Investment Casting:
- Process Overview:
- Pattern Creation: A wax or plastic pattern is created based on the final part design.
- Assembly: Multiple wax patterns are attached to a central wax sprue to form a cluster (tree).
- Coating: The wax cluster is repeatedly dipped in ceramic slurry to build a ceramic shell around it.
- Burnout: The ceramic-coated assembly is heated to melt and remove the wax, leaving a hollow ceramic mold.
- Pouring: Molten metal is poured into the mold cavity.
- Finishing: After solidification, the ceramic shell is broken away, and the final part is cleaned and finished as required.
- Advantages:
- Complex Shapes: Can produce parts with complex geometries, thin walls, and fine details.
- Surface Finish: Excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
- Material Versatility: Supports a wide range of metals and alloys.
- Minimal Machining: Often requires minimal post-processing due to near-net shape casting.
- Applications:
- Aerospace: Turbine blades, engine components.
- Medical: Surgical instruments, implants.
- Automotive: Engine parts, brackets.

CNC Mineral Casting:
- Process Overview:
- Material: Typically uses mineral-filled epoxy resin, which is poured into a mold.
- Curing: The resin is cured to form a solid mineral casting with embedded granite or quartz aggregates.
- Machining: After curing, the casting is machined using CNC processes to achieve final dimensions and surface finish.
- Assembly: Components like machine beds, columns, and bases for precision machinery are often produced.
- Advantages:
- Damping Properties: Excellent vibration damping and high rigidity.
- Thermal Stability: Maintains dimensional stability over a wide range of temperatures.
- Design Flexibility: Allows for complex shapes and integrated features.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces machining time and waste compared to traditional cast iron.
- Applications:
- Machine Tools: CNC machine beds, columns, bases.
- Metrology Equipment: Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs).
- Industrial Applications: Semiconductor manufacturing equipment, optical devices.
Comparison:
- Material: Investment casting uses metals/alloys, while CNC mineral casting uses epoxy resin with mineral fillers.
- Complexity: Investment casting excels in intricate details and thin walls. CNC mineral casting offers structural stability and damping.
- Cost: Initial tooling costs are higher for investment casting, but it can be cost-effective for high-volume production. CNC mineral casting can be more economical for low to medium volumes due to reduced machining.
- Application: Investment casting is ideal for precise metal parts with fine details. CNC mineral casting is preferred for machine components requiring stability and vibration damping.