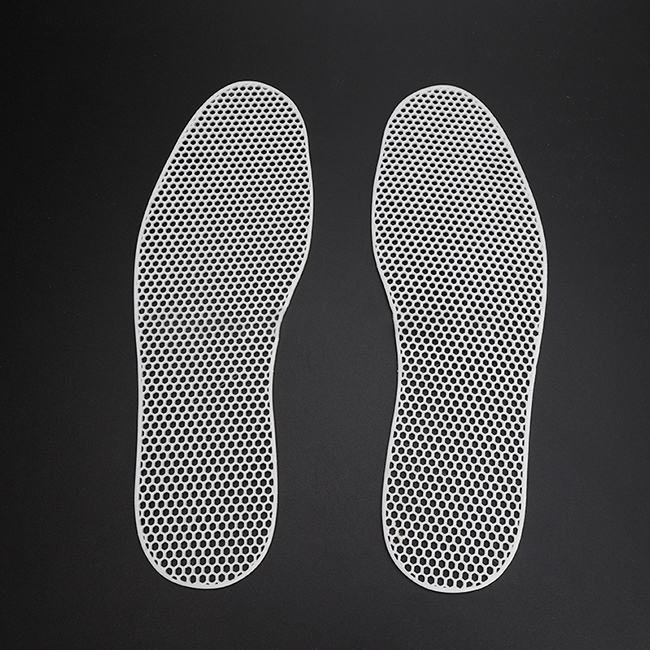
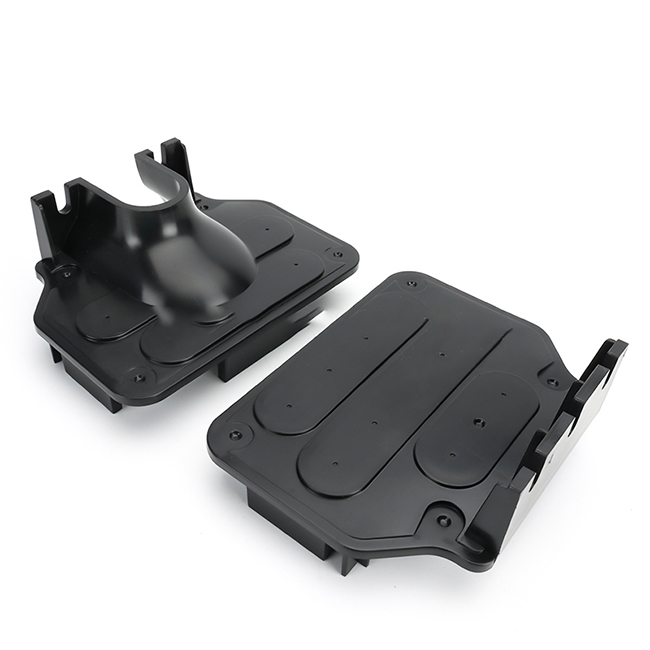
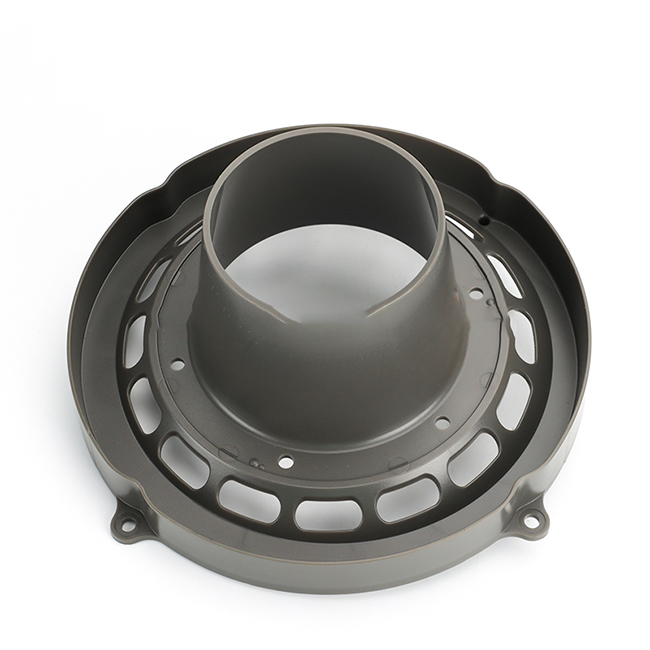
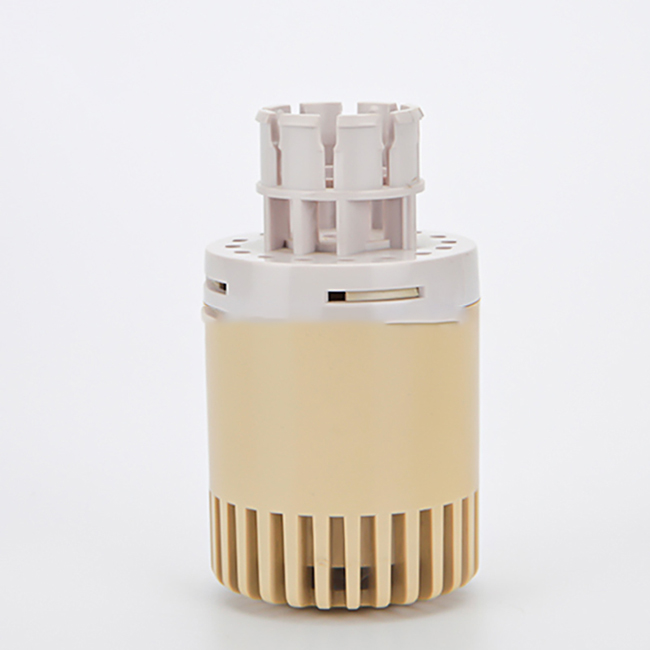
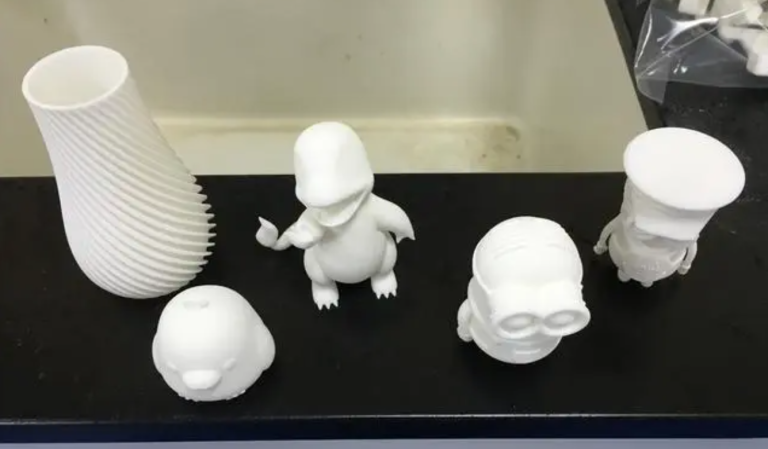
Designing injection molded plastic parts involves several key considerations to ensure successful manufacturing and optimal performance of the final product. Here are some important aspects to keep in mind:
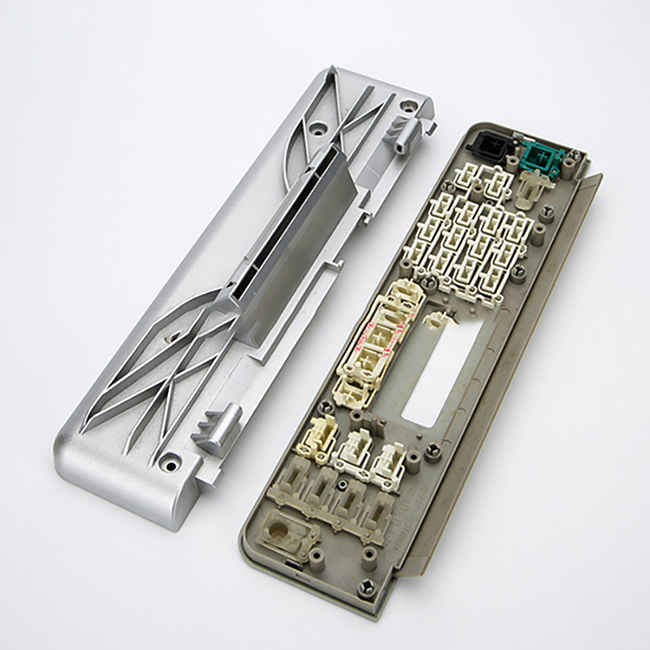

1.Part Geometry: The geometry of the part should be carefully designed to facilitate the injection molding process. This includes minimizing the use of undercuts, sharp corners, and thin walls, which can increase complexity and cost. Instead, incorporate draft angles, fillets, and ribs to improve moldability and structural integrity.
2.Wall Thickness: Maintain uniform wall thickness throughout the part to prevent defects such as sink marks, warpage, and voids. Avoid abrupt changes in thickness, as this can lead to uneven cooling and part distortion.
3.Rounded Corners and Fillets: Incorporating rounded corners and fillets helps reduce stress concentrations and improves mold flow, resulting in stronger and more aesthetically pleasing parts.
4.Ribs and Gussets: Use ribs and gussets to reinforce the part and prevent warping or deformation. These features add strength and rigidity without significantly increasing material usage.
5.Draft Angles: Apply draft angles to vertical walls to facilitate easy ejection of the part from the mold. Typical draft angles range from 1 to 3 degrees per side, depending on the material and surface finish requirements.
6.Surface Finish: Consider the desired surface finish of the part and specify appropriate textures or finishes on the mold surface. Smooth surfaces require polished molds, while textured surfaces can be achieved with etching or abrasive blasting techniques.
7.Material Selection: Choose the right plastic resin based on the application requirements, including mechanical properties, chemical resistance, temperature stability, and cost. Common materials used in injection molding include ABS, polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), and nylon.
8.Gate Placement: Strategically position gates (entry points for molten plastic) to minimize visible marks on the finished part and ensure proper filling of the mold cavity. Gate design options include edge gates, pin gates, and hot runner systems.
9.Mold Design Considerations: Collaborate with mold designers to optimize the mold layout, cooling channels, ejector system, and venting to maximize productivity and part quality.
10.Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy: Define tolerances and dimensional specifications to meet functional requirements and ensure interchangeability of parts in assembly.
By carefully considering these design factors, engineers can create injection molded plastic parts that are both manufacturable and meet the performance criteria for their intended application. Collaboration between design, engineering, and manufacturing teams is crucial to achieving success in injection molding projects.